|
AP Statistics Chapter 2 - The Normal Distributions
2.1: Density Curves and the Normal Distributions
Density Curve
A density curve is a curve that
- is always on or above the horizontal axis, and
- has area exactly 1 underneath it.
A density curve describes the overall pattern of a distribution. The area under the curve and above any range of values is the proportion of all observations that fall in the range.
Median and Mean of a Density Curve
The median of a density curve is the equal-areas point, the point that divides the area under the curve in half.
The mean of a density curve is the balance point, at which the curve would balance if made of solid material.
The median and mean are the same for a symmetric density curve. They both lie at the center of the curve. The mean of a skewed curve is pulled away from the median in the direction of the long tail.
Normal Distributions
A normal distribution is a curve that is
- mound-shaped
- symmetric
- based on a continuous variable
- adheres to the 68-95-99.7 Rule
The 68-95-99.7 Rule
In the normal distribution with mean m and standard deviation s:
- 68% of the observations fall within s of the mean m.
- 95% of the observations fall within 2s of the mean m.
- 99.7% of the observations fall within 3s of the mean m.
2.2: Standard Normal Calculations
Standardizing and z-Scores
If x is an observation from a distribution that has mean m and standard deviation s, the standardized value of x is
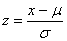
A standardized value is often called a z-score.
Standard Normal Distribution
The standard normal distribution is the normal distribution N(0, 1) with mean 0 and standard deviation 1.
If a variable x has any normal distribution N(m, s) with mean m and standard deviation s, then the standardized variable
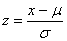
has the standard normal distribution.
The Standard Normal Table
Table A is a table of areas under the standard normal curve. The table entry for each value z is the area under the curve to the left of z.
Click here for an online version of Table A (the z-score table).
|
