Multiple Choice
Identify the
choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
An opinion poll asks a random sample of adults whether they favor banning
ownership of handguns by private citizens. A radio commentator believes that more than half of all
adults favor such a ban. The null and alternative hypotheses you would use to test this claim
are
|
|
|
2.
|
DDT is an insecticide that accumulates up the food
chain. Predator birds can be contaminated with quite high levels of the chemical by eating many
lightly contaminated prey. One effect of DDT upon birds is to inhibit the production of the enzyme
carbonic anhydrase, which controls calcium metabolism. It is believed that this causes eggshells to
be thinner and weaker than normal and makes the eggs more prone to breakage. (This is one of the
reasons why the condor in California is near extinction.) An experiment was conducted where 16
sparrow hawks were fed a mixture of 3 ppm dieldrin and 15 ppm DDT (a combination often found in
contaminated prey). The first egg laid by each bird was measured, and the mean shell thickness was
found to be 0.19 mm. A “normal” eggshell has a mean thickness of 0.2 mm.
The null and alternative hypotheses are
|
|
|
3.
|
A significance test allows you to reject a null hypothesis H0 in
favor of an alternative Ha at the 5% significance level. What can you say about
significance at the 1% level?
a) | There is sufficient evidence to reject H0 at the 1% significance
level. | b) | Ha can be rejected at the 1% significance level. | c) | The answer
can’t be determined from the information given. | d) | H0 can be rejected at the 1%
significance level. | e) | There is insufficient evidence to reject
H0 at the 1% significance level. |
|
|
|
4.
|
A random sample of 100 likely voters in a small city produced 59 voters in favor
of Candidate A. The observed value of the test statistic for testing the null hypothesis
H 0: 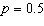 versus the alternative H a: 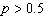 is
|
|
|
5.
|
We wish to see if the dial indicating the oven
temperature for a certain model oven is properly calibrated. Four ovens of this model are selected at
random. The dial on each oven is set to 300° F. After one hour, the actual temperature of
each oven is measured. The temperatures observed are 305°, 310°, 300°, and 305°
which result in 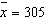 and and 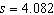 . Assuming that the actual
temperatures for this model when the dial is set to 300° are normally distributed with mean
m, we test whether the dial is properly calibrated by testing the
hypotheses H0: m = 300,
Ha: m ¹
300. . Assuming that the actual
temperatures for this model when the dial is set to 300° are normally distributed with mean
m, we test whether the dial is properly calibrated by testing the
hypotheses H0: m = 300,
Ha: m ¹
300.
Based on the data, the value of the one-sample
t statistic is
a) | 5. | b) | 4.90. | c) | 2.82. | d) | 2.45. | e) | 1.23. |
|
|
|
6.
|
Sheldon takes a random sample of 50 U.S. housing units and finds that 30 are
owner-occupied. Using a significance test for a proportion, he is not able to reject the null
hypothesis that exactly half of U.S. housing units are owner-occupied. Later, Sheldon learns that the
U.S. Census for that same year found that 66.2% of housing units are owner-occupied. Select the best
description of the type of error in this situation.
a) | A Type I error was made because a false null hypothesis wasn’t
rejected. | b) | A Type I error was made because a false null hypothesis was
rejected. | c) | A Type II error was made because a false null hypothesis wasn’t
rejected. | d) | A Type II error was made because a false null hypothesis was
rejected. | e) | No error was made. |
|
|
|
7.
|
The one sample t statistic from a sample of
n = 15 observations for the one-sided test of
H0: m = 8,
Ha: m > 8 has the
value t = 2.19. Based on this information, which of the following would be true?
a) | 0.05 < P-value <
0.10. | b) | 0.025 < P-value <
0.05. | c) | 0.02 < P-value <
0.025. | d) | 0.01 < P-value <
0.02. | e) | 0.005 <
P-value < 0.01. |
|
|
|
8.
|
Which of the following conditions are not
necessary for the use of the one-proportion z procedures?
a) | 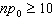 | b) | 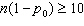 | c) | the data must be a random sample from the population of
interest | d) | The population size is at least 10 times greater than
the size of the sample | e) | All of these
conditions are necessary |
|
|
|
9.
|
Which of the following conditions are not
necessary for the use of the t procedures?
a) | the population standard deviation is
unknown | b) | the population distribution is Normal or we have a large
sample size | c) | the data must be
an SRS from the population | d) | np0
and n(1 – p0) are both at least 10 | e) | All of these conditions are necessary |
|
|
|
10.
|
Resting pulse rate is an important measure of the
fitness of a person's cardiovascular system, with a lower rate indicative of greater fitness.
The mean pulse rate for all adult males is approximately 72 beats per minute. A random sample of 25
male students currently enrolled in the Faculty of Agriculture was selected and the mean resting
pulse rate was found to be 80 beats per minute with a standard deviation of 20 beats per minute. The
experimenter wishes to test if the students are less fit, on average, than the general
population.
A possible Type I error here would be
to
a) | conclude that the students are less fit (on average)
than the general population when in fact they have equal fitness on
average. | b) | conclude that the students have the same fitness (on
average) as the general population when in fact they are less fit (on
average). | c) | conclude that the students have the same fitness (on
average) as the general population when in fact they have the same fitness (on
average). | d) | conclude that the students are less fit (on average)
than the general population, when, in fact, they are less fit (on
average). | e) | conclude that the students have the same fitness (on
average) when in fact they are more fit (on average). |
|